![]()
Introducing Windows Communication
Foundation
An Early Look
David Chappell, Chappell & Associates
September 2005
© Copyright Microsoft Corporation 2005. All rights reserved.
Describing Windows Communication Foundation
Illustrating the Problem: A Scenario
Addressing the Problem: What WCF Provides
Unification of Microsoft’s Distributed Computing Technologies
Interoperability with Applications Built on Other Technologies
Explicit Support for Service-Oriented Development
Using Windows Communication Foundation
Tool Support: WCF and Visual Studio
Describing Windows Communication Foundation
The global embrace of Web services—standard protocols for application-to-application communication—has changed software development. The functions that Web services can now provide, including effective security, distributed transactions, and reliable communication, enable this single technology family to address what were once separate problems. And the new view of services as a distinct software abstraction provides a solid foundation for the service-oriented architecture (SOA) that many organizations are putting in place.
Software development environments must keep pace with these changes. The benefits Web services bring should be reflected in the tools and technologies that developers use. Going forward, a simpler approach to distributed computing, broad interoperability, and direct support for service-orientation will be fundamental for developers. Windows Communication Foundation (WCF), Microsoft’s forthcoming technology for service-oriented applications, is designed to address these requirements. Originally code-named “Indigo”, WCF is implemented in managed code as an extension of the Microsoft .NET Framework 2.0. Once it’s available, this technology is intended to be the foundation for creating service-oriented applications on Windows[1].
Illustrating the Problem: A Scenario
To get a sense of the problems that WCF addresses, suppose that a car rental firm decides to create a new application for reserving cars. Since this application will run on Windows, the firm chooses to build it on version 2.0 of the .NET Framework. The architects of this rental car reservation application know that the business logic it implements will need to be accessible by other software running both inside and outside their company. Accordingly, they decide to build it in a service-oriented style, with the application’s logic exposed to other software through a well-defined set of services. To implement these services, and thus communicate with other software, the new application will use WCF.
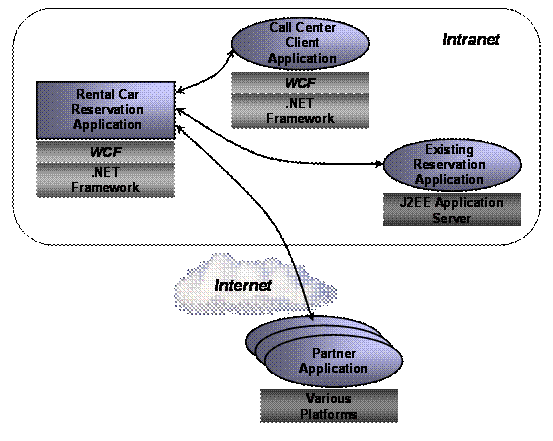
Over its lifetime, the rental car reservation application will likely be accessed by a range of other applications. When it’s designed, however, the architects of the rental car reservation application know that its business logic will be accessed, as shown in the figure above, by three other kinds of software:
n A call center client application running on Windows desktops that will be used by employees in the organization’s call center. Created specifically for the new reservations system, this application will also be built using the .NET Framework and WCF. (In some sense, this application isn’t truly distinct from the new rental car reservation application, since its only purpose is to act as a client for the new system. Still, from a service-oriented perspective, it’s just another client for the reservation system’s business logic.)
n An existing reservation application built on a J2EE server running on a non-Windows system. Due to a recent merger with another car rental firm, this existing system must be able to access the new application’s logic to provide customers of the merged firms with a unified experience.
n Partner applications running on a variety of platforms, each located within a company that has a business arrangement with the car rental firm. Partners might include travel agencies, airlines and others that have a business requirement to make car rental reservations.
The diverse communication requirements for the new rental car reservation application aren’t simple. For interactions with the call center client application, for instance, performance is paramount, while interoperability is straightforward, since both are built on the .NET Framework. For communication with the existing J2EE-based reservation application and with the diverse partner applications, however, interoperability becomes the highest goal. The security requirements are also quite different, varying across local Windows-based applications, a J2EE-based application running on another operating system, and a variety of partner applications coming in across the Internet. Even transactional requirements might vary, with only the internal applications being allowed to make transactional requests. How can these diverse business and technical requirements be met without exposing the creators of the new application to unmanageable complexity?
The answer to this question is WCF. Designed for exactly this kind of diverse but realistic scenario, WCF will be the default technology for Windows applications that expose and access services. This paper provides an introduction to WCF, examining what it provides and showing how it’s used. Throughout this introduction, the scenario just described will serve as an example. The goal is to make clear what WCF is, show what problems it solves, and illustrate how it solves those problems.
Addressing the Problem: What WCF Provides
The foundation for new Windows-based applications is the .NET Framework. Accordingly, WCF is implemented primarily as a set of classes on top of the .NET Framework’s Common Language Runtime (CLR). Because it extends their familiar environment, WCF allows developers who create object-oriented applications using the .NET Framework today to also build service-oriented applications in a familiar way.

The figure above shows a simple view of a WCF client and service. The two interact via SOAP, WCF’s native protocol, so even though the figure shows both parties built on WCF, this certainly is not required. WCF is built on version 2.0 of the .NET Framework, which is scheduled for release in late 2005. WCF itself will ship as part of the WinFX developer platform included with Windows Vista and scheduled for release in 2006. WinFX, including WCF, will also be made available on Windows XP and Windows Server 2003.
As the scenario described earlier suggests, WCF addresses a range of problems for communicating applications. Three things stand out, however, as WCF’s most important aspects:
n Unification of existing .NET Framework communication technologies
n Support for cross-vendor interoperability, including reliability, security, and transactions
n Explicit service orientation
The following sections describe what WCF offers in each of these areas.
Unification of Microsoft’s Distributed Computing Technologies
Think about the team of developers implementing the rental car reservation application described earlier. In the absence of WCF, this team would need to choose the right distributed technology from the multiple choices offered by the .NET Framework. Yet given the diverse requirements of this application, no single technology would fit the bill. Instead, the application would probably use multiple existing .NET technologies. For example:
n ASMX, also called ASP.NET Web Services, would be an option for communicating with the J2EE-based existing reservation application and with the partner applications across the Internet. Given that basic Web services are supported today on most platforms, this would likely be the most direct way to achieve cross-vendor interoperability.
n .NET Remoting is a natural choice for communication with the call center application, since both are built on the .NET Framework. Remoting is designed expressly for .NET-to-.NET communication, so it would offer the best performance for this situation.
n Enterprise Services (the successor to COM+) might be used by the rental car reservation application for things such as managing object lifetimes and defining distributed transactions. These functions could be useful in communicating with any of the other applications in this scenario, but Enterprise Services supports only a limited set of communication protocols.
n Web Services Enhancements (WSE) could be used along with ASMX to communicate with the J2EE-based reservation application and with the partner applications. Because it implements more recently defined Web services agreements, known collectively as the WS-* specifications, WSE can allow better security and more, as long as all applications involved support compatible versions of these new specifications.
n Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ) could be used to communicate with Windows-based partner applications that weren’t always available. The persistent queuing that MSMQ provides is typically the best solution for intermittently connected applications.
If it were built on today’s .NET Framework, the rental car reservation application would need to use more than one of these communication technologies, and maybe even all five, to meet its requirements. Although this is technically possible, the resulting application would be complex to implement and challenging to maintain. A better solution is needed.

With WCF, this solution is at hand. As the figure above shows, WCF can be used for all the situations described above. Accordingly, the rental car reservation application can use this single technology for all its application-to-application communication. Here’s how WCF addresses each of these requirements:
n Because WCF can communicate using Web services, interoperability with other platforms that also support SOAP, such as the leading J2EE-based application servers, is straightforward.
n To allow optimal performance when both parties in a communication are built on WCF, the wire encoding used in this case is an optimized binary version of SOAP. Messages still conform to the data structure of a SOAP message, referred to as its Infoset, but their encoding uses a binary representation of that Infoset rather than the standard angle-brackets-and-text format of XML. Using this option would make sense for communicating with the call center client application, since it’s also built on WCF, and performance is a paramount concern.
n Managing object lifetimes, defining distributed transactions, and other aspects of Enterprise Services are now provided by WCF. They are available to any WCF-based application, which means that the rental car reservation application can use them with any of the other applications it communicates with.
n Because it supports a large set of the WS-* specifications, WCF helps provide reliability, security, and transactions when communicating with any platform that also supports these specifications.
n WCF’s option for queued messaging, built on MSMQ, allows applications to use persistent queuing without needing to use another set of application programming interfaces.
The result of this unification is greater functionality and significantly reduced complexity. Because WCF allows an application to address all the communication requirements listed earlier, it can easily support scenarios that were difficult (or even impossible) with the collection of technologies that preceded it. While Microsoft will still support these earlier technologies, most new applications that would previously have used any of them will instead be built on WCF.
Interoperability with Applications Built on Other Technologies
While WCF introduces a new development environment for distributed applications, it’s designed to interoperate well with the non-WCF world. There are two important aspects to WCF interoperability: interoperability with platforms created by other vendors, and interoperability with the Microsoft technologies that preceded WCF. The following section describes both.
Interoperability with Other Web Services Platforms
Enterprises today typically have systems and applications that were purchased from a range of vendors. In the rental car application, for instance, communication is required with various other software applications written in various languages and running on various operating systems. This kind of diversity is the reality in most organizations, and it will remain so for the foreseeable future.
Because WCF’s fundamental communication mechanism is SOAP, WCF-based applications can communicate with other software running in a variety of contexts. As shown in the figure below, an application built on WCF can interact with all of the following:
n WCF-based applications running in a different process on the same Windows machine
n WCF-based applications running on another Windows machine
n Applications built on other technologies, such as J2EE application servers, that support standard Web services. These applications can be running on Windows machines or on machines running other operating systems, such as Sun Solaris, IBM z/OS, or Linux.
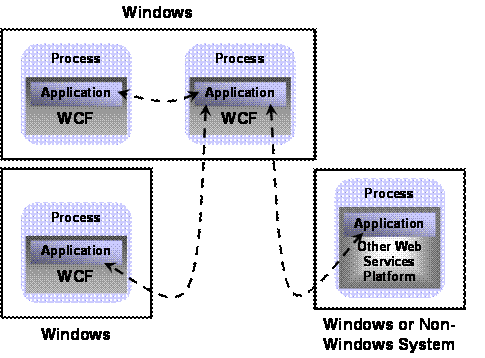
To allow more than just basic communication, WCF implements Web services technologies defined by the WS-* specifications. All of these specifications were originally defined by Microsoft, IBM, and other vendors working together. As the specifications become stable, ownership often passes to standards bodies such as the Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards (OASIS). As the figure on the next page shows, these specifications address several areas, including basic messaging, security, reliability, transactions, and working with a service’s metadata.

WCF supports all the specifications shown in this figure. Grouped by function, those specs are:
n Messaging: SOAP is the foundation protocol for Web services, defining a basic envelope containing a header and a body. WS-Addressing defines additions to the SOAP header for addressing SOAP messages, which frees SOAP from relying on the underlying transport protocol, such as HTTP, to carry addressing information. The Message Transmission Optimization Mechanism (MTOM) defines an optimized transmission format for SOAP messages based on the XML-binary Optimized Packaging (XOP) specification.
n Metadata: The Web Services Description Language (WSDL) defines a standard language for specifying services and various aspects of how those services can be used. WS-Policy allows specification of more dynamic aspects of a service’s behavior that cannot be expressed in WSDL, such as a preferred security option. WS-MetadataExchange allows a client to directly request descriptive information about a service, such as its WSDL and its policies, via SOAP.
n Security: WS-Security, WS-Trust and WS-SecureConversation all define additions to SOAP messages for providing authentication, data integrity, data privacy and other security features.
n Reliability: WS-ReliableMessaging defines additions to the SOAP header that allow reliable end-to-end communication, even when one or more SOAP intermediaries must be traversed.
n Transactions: Built on WS-Coordination, WS-AtomicTransaction allows using two-phase commit transactions with SOAP-based exchanges.
The rental car reservation application would likely use several of these more advanced technologies. For example, WS-Addressing is essential whenever SOAP is running over a protocol other than HTTP, which might be the case for communication with the .NET Framework-based call center client application. WCF relies on WS-Policy and WS-MetadataExchange to discover whether the system it’s communicating with is also using WCF and for other things. Reliable communication is essential for most situations, so it’s likely that WS-ReliableMessaging would be used to interact with many of the other applications in this scenario. Similarly, WS-Security and the related specifications might also be used for communication with one or more of the applications, since all would require some kind of security. For the applications that are allowed to use transactions with the rental car reservation system, WS-AtomicTransaction would be essential. Finally, MTOM could be used whenever an optimized wire format made sense, and both sides of the communication supported this option.
The key point is that WCF implements interoperable Web services, complete with cross-platform security, reliability, transactions, and more. To avoid paying an unnecessary performance penalty, WCF-to-WCF communication is optimized, but all other communication uses standard Web services protocols on the wire. In fact, as described later, it’s possible — easy, even — for a single application to expose its services to both kinds of clients.
Interoperability with Microsoft’s Pre-WCF Technologies
Many of Microsoft’s customers have made significant investments in the .NET Framework technologies that WCF subsumes. Protecting those investments was a fundamental goal of WCF’s designers. Installing WCF doesn’t break existing technology, so there’s no requirement that organizations change existing applications to use it. A clear upgrade path is provided, however, and wherever possible, WCF interoperates with those earlier technologies.
For example, both WCF and ASMX use SOAP, so WCF-based applications can directly interoperate with those built on ASMX. Existing Enterprise Services applications can also be wrapped with WCF interfaces, allowing them to interoperate with applications built on WCF. And because WCF’s persistent queuing relies on MSMQ, WCF-based applications can interoperate directly with non-WCF-based applications built using native MSMQ interfaces such as System.Messaging. In the rental car reservations application, software built using any of these earlier technologies could directly connect to and use the new system’s WCF-based services.
Interoperability isn’t always possible, however. For example, even though WSE 1.0 and WSE 2.0 implement some of the same WS-* specifications as WCF, these earlier technologies implement earlier versions of the specs. Version 3.0 of WSE 3.0 does allow interoperability with WCF, but earlier versions do not. For more on interoperability with existing .NET Framework technologies, see the section “Coexistence and Upgrade” later in this paper.
Explicit Support for Service-Oriented Development
Over the next few years, creating applications in a service-oriented style will become the norm. For this to happen, the platforms on which those applications are built must provide the right support for creating service-oriented software. Achieving this is one of WCF’s most important goals.
Thinking of an application as providing and consuming services is hardly a new idea. What is new is a clear focus on services as distinct from objects. Toward this end, WCF’s creators kept four tenets in mind during the design of this technology:
n Share schema, not class. Unlike older distributed object technologies, services interact with their clients only through a well-defined XML interface. Behaviors such as passing complete classes, methods and all, across service boundaries aren’t allowed.
n Services are autonomous. A service and its clients agree on the interface between them, but are otherwise independent. They may be written in different languages, use different runtime environments, such as the CLR and the Java Virtual Machine, execute on different operating systems, and differ in other ways.
n Boundaries are explicit. A goal of distributed object technologies such as Distributed COM (DCOM) was to make remote objects look as much as possible like local objects. While this approach simplified development in some ways by providing a common programming model, it also hid the inescapable differences between local objects and remote objects. Services avoid this problem by making interactions between services and their clients more explicit. Hiding distribution is not a goal.
n Use policy-based compatibility. When possible, determining which options to use between systems should rely on mechanisms defined in languages such as WSDL and WS-Policy. The ability for a client to consume a service is based on the intersection of what the client supports and what the service supports.
Service-oriented applications are the successor to the multi-tier applications of the past ten years. As the architectural style spreads, this approach will become the default for a majority of new enterprise software. Because WCF will be the foundation for service-oriented applications built on the .NET Framework, it will become a mainstream technology for Windows-based software.
Using Windows Communication Foundation
The best way to understand what it’s like to use WCF is to dive in and look at the code. This section shows what’s required to create and consume a simple WCF service. Once again, the service used as an example is drawn from the rental car reservation application described earlier.
Creating a WCF Service
As the figure on the next page shows, every WCF service is constructed from three things:
n A service class, implemented in C# or Visual Basic or another CLR-based language, that implements one or more methods
n A host environment — an application domain and process — in which the service runs
n One or more endpoints that allow clients to access the service. All communication with a WCF service happens via the service’s endpoints.
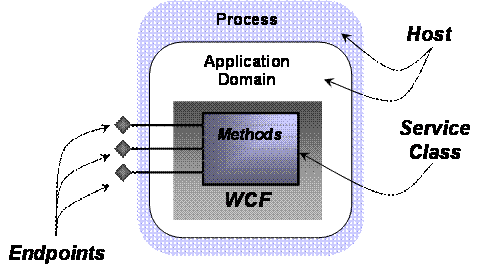
Understanding WCF requires grasping all these concepts. This section describes each one, beginning with service classes.
Creating a Service Class
A WCF service class is a class like any other, but it has a few additions. These additions allow the class’s creator to define one or more contracts that this class implements. Each WCF service class implements at least one service contract, which defines the operations this service exposes. A service class might also provide an explicit data contract, which defines the data those operations convey. This section looks at both, beginning with service contracts.
Defining Service Contracts
Every WCF service class implements methods for its clients to use. The creator of a service class determines which of its methods are exposed as client-callable operations by specifying that they are part of some service contract. Defining service contracts—in fact, working explicitly with services in general—is largely a new idea for the .NET world. WCF’s designers needed to find a way to graft this idea on top of the CLR and the programming languages built on it. Fortunately, the CLR’s creators anticipated the need for extensions like this, so they provided support for attributes. As seen by a developer, attributes are character strings, perhaps with associated properties, that can appear before a class definition, a method definition, and in other places. Wherever an attribute appears, it changes some aspect of the behavior of the thing it is associated with.
The .NET Framework has used attributes for various things since its initial release. For example, to mark a method as a SOAP-callable Web service in the Framework’s ASMX technology, that method is preceded by the WebMethod attribute. Similarly, Enterprise Services uses the Transaction attribute to indicate that a method requires a transaction. WCF applies this idea to services, defining a group of attributes to define and control services.
The most fundamental attribute in WCF is ServiceContract. In fact, a WCF service class is just a class that either is itself marked with the ServiceContract attribute or implements an interface marked with this attribute. Both options make sense in different situations, and both will be described shortly.
First, however, here’s a short description of the class, called RentalReservations, that will be used as an example throughout this section. It’s an implementation of the basic functions in the car rental reservation application described earlier, and it has four methods:
n Check, which allows a client to determine the availability of a particular vehicle class at a certain location on specific dates. This method returns a Boolean value indicating whether there is availability.
n Reserve, which allows a client to reserve a particular class of vehicle at a certain location on specific dates. This method returns a confirmation number.
n Cancel, which allows a client to cancel an existing reservation by providing its confirmation number. This method returns a Boolean value indicating whether the cancellation succeeded.
n GetStats, which returns a count of how many reservations currently exist. Unlike the other methods in this class, GetStats can only be invoked by a local administrator, not by clients of the service.
With this in mind, here’s an abbreviated C# example that uses the class-based approach to define RentalReservations as a WCF service class:
using System.ServiceModel;
[ServiceContract]
class RentalReservations
{
[OperationContract]
public bool Check(int vehicleClass, int location, string dates)
{
bool availability;
// logic to check availability goes here
return availability;
}
[OperationContract]
private int Reserve(int vehicleClass, int location,
string dates)
{
int confirmationNumber;
// logic to reserve rental car goes here
return confirmationNumber;
}
[OperationContract]
private bool Cancel(int confirmationNumber)
{
bool success;
// logic to cancel reservation goes here
return success;
}
public int GetStats()
{
int numberOfReservations;
// logic to get the current number of reservations goes here
return numberOfReservations;
}
}
The ServiceContract attribute and all the other attributes that this example uses are defined in the System.ServiceModel namespace, so the code begins with a using statement that references this namespace. Each method in a service class that can be invoked by a client must be marked with another attribute named OperationContract. All the methods in a service class that are preceded by the OperationContract attribute are automatically exposed by WCF as SOAP-callable operations. In this example, Check, Reserve, and Cancel are all marked with this attribute, so all three are exposed to clients of this service. Any methods in a service class that aren’t marked with OperationContract, such as GetStats in the example above, aren’t included in the service contract, and so can’t be called by clients of this WCF service.
The example shown above illustrates the simplest way to create a WCF service class: marking a class directly with ServiceContract. When this is done, the class’s service contract is implicitly defined to consist of all methods in that class that are marked with OperationContract. It’s also possible (and often better) to specify service contracts explicitly using a language’s interface type. Using this approach, the RentalReservations class might look like this:
using System.ServiceModel;
[ServiceContract]
interface IReservations
{
[OperationContract]
bool Check(int vehicleClass, int location, string dates);
[OperationContract]
int Reserve(int vehicleClass, int location, string dates);
[OperationContract]
bool Cancel(int confirmationNumber);
}
class RentalReservations : IReservations
{
public bool Check(int vehicleClass, int location, string dates)
{
bool availability;
// logic to check availability goes here
return availability;
}
public int Reserve(int vehicleClass, int location, string dates)
{
int confirmationNumber;
// logic to reserve rental car goes here
return confirmationNumber;
}
public bool Cancel(int confirmationNumber)
{
bool success;
// logic to cancel reservation goes here
return success;
}
public int GetStats()
{
int numberOfReservations;
// logic to determine the current number of reservations goes here
return numberOfReservations;
}
}
In this example, the ServiceContract and OperationContract attributes are assigned to the IReservations interface and the methods it contains rather than to the RentalReservations class itself. The result is the same, however, so this version of the service exposes the same service contract as the previous one. It’s worth noting that the object contract this class exposes is not the same, however. Because interfaces can’t generally contain private methods, all the methods defined in the interface, including Reserve and Cancel, are public.
Using explicit interfaces like this is slightly more complicated, but it allows more flexibility. For example, a class can implement more than one interface, which means that it can also implement more than one service contract. By exposing multiple endpoints, each with a different service contract, a service class can present different groups of services to different clients.
Marking a class or interface with ServiceContract and one or more of its methods with OperationContract also allows automatically generating service contract definitions in WSDL. Accordingly, the externally visible definition of every WCF service contract can be accessed as a standard WSDL document specifying the operations in that contract. This style of development, commonly called code-first, allows creating a standard interface definition directly from types defined in programming languages such as C# or Visual Basic.
An alternative approach is contract-first development, an option that WCF also supports. In this case, a developer typically starts with a WSDL document describing the interface (i.e., the contract) that a service class must implement. Using a tool called svcutil, which is described later in this paper, a developer can generate a skeleton service class directly from a WSDL document. This approach is especially useful for implementing externally defined WSDL interfaces, such as those created by industry organizations.
Defining Data Contracts
A WCF service class specifies a service contract that defines which of its methods are exposed to clients of that service. Each of those operations will typically convey some data, which means that a service contract also implies some kind of data contract describing the information that will be exchanged. In some cases, this data contract is defined implicitly as part of the service contract. For example, in the RentalReservations classes shown above, all the methods have parameters and return values of simple types, such as integer, string, and Boolean. For services similar to this one, where every operation uses only simple types, it makes sense to define the data aspects of their contract implicitly within the service contract. There’s no need for anything else.
But services can also have parameters of more complex types, such as structures. In cases like this, an explicit data contract is required. Data contracts define how in-memory types are converted to a form suitable for transmission across the wire, a process known as serialization. In effect, data contracts are a mechanism for controlling how data is serialized.
In a WCF service class, a data contract is defined using the DataContract attribute. A class, structure, or other type marked with DataContract can have one or more of its members preceded by the DataMember attribute, indicating that this member should be included in a serialized value of this type. For example, suppose the parameter lists of Check and Reserve in the RentalReservations class were changed to be a structure containing the same information. To pass this structure as a parameter using WCF requires defining it as a data contract, like this:
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
[DataContract]
struct ReservationInfo {
[DataMember] public int vehicleClass;
[DataMember] public int location;
[DataMember] public string dates;
}
Unlike the attributes shown so far, those used for data contracts are defined in the System.Runtime.Serialization namespace. Accordingly, this simple type definition begins with a using statement for this namespace. When an instance of the ReservationInfo type shown here is passed as a parameter in a method marked with OperationContract, all the fields marked with the DataMember attribute — which in this case is all three of them — will be passed. If any of the fields were not marked with this attribute, they would not be transmitted when this type was passed as a parameter.
Whether a field is labeled as public or private has no effect on whether it is serialized. Just as with methods, the public and private keywords are part of the contract defining how this type can be accessed by other objects in the same application. DataMember, like OperationContract, defines how the type can be accessed by clients of the service this class implements. Once again, the two are completely distinct.
One final point worth emphasizing about WCF contracts is that nothing becomes part of either a service contract or a data contract by default. Instead, a developer must explicitly use the ServiceContract and DataContract attributes to indicate which types have WCF-defined contracts, and then explicitly specify which parts of those types are exposed to clients of this service using the OperationContract and DataMember attributes. One of WCF’s design tenets was that services should have explicit boundaries, so WCF is an opt-in technology. Everything a service makes available to its clients is expressly specified in the code.
Selecting a Host
A class implementing a WCF service is typically compiled into a library. By definition, all libraries need a host application domain and Windows process to run in. WCF provides two main options for hosting libraries that implement services. One is to use a host application domain and process provided by either Internet Information Services (IIS) or a related technology in Windows Vista called the Windows Activation Service (WAS). The other allows a service to be hosted in any application domain running in an arbitrary process. The following section describes both options, beginning with the IIS/WAS approach
Hosting a Service Using Internet Information Services or the Windows Activation Service
The simplest way to host a WCF service is to rely on IIS or WAS. Both rely on the notion of a virtual directory, which is just a shorter alias for an actual directory path in the Windows file system.
To see how hosting with IIS and WAS works, suppose either of the RentalReservations classes shown earlier was compiled into the library reserve.dll, then placed in the virtual directory reservation on a system running Windows Server 2003. To indicate that the WCF service implemented in reserve.dll should be hosted by IIS or WAS, a developer creates a file in the reservation virtual directory with the extension .svc (which stands, of course, for “service”). For our simple example, this file might be called reserve.svc, and its entire contents could be:
<% language=c# class="RentalReservations" %>
Once this has been done and an endpoint has been defined as shown in the next section, a request from a client to one of the RentalReservations service’s methods will automatically create an instance of this class to execute the specified operation. That instance will run in an application domain created within the standard process that IIS or WAS provides.
Because it provides a standalone activation service, WAS allows hosting WCF services without running a full-blown web server. And while hosting WCF services in IIS looks just like hosting them in WAS, as shown above, there are a couple of significant differences:
n IIS-hosted WCF services can only be accessed using SOAP over HTTP. No other transport protocols are supported.
n Although WAS doesn’t require a Web server to be installed on the system, WCF services hosted in IIS obviously do.
Whatever choice is made, both WAS and IIS provide WCF services with a range of support, such as the ability to configure automatic process recycling.
Hosting a Service in an Arbitrary Process
Relying on IIS or WAS to provide a process for hosting a WCF service is certainly the simplest choice. Yet applications often need to expose services from their own process rather than relying on one provided by Windows. Fortunately, this isn’ t hard to do. The following example shows how to create a simple console application that hosts either of the RentalReservations classes defined earlier:
using System.ServiceModel;
public class ReservationHost
{
public static void Main()
{
ServiceHost s =
new ServiceHost(typeof(RentalReservations));
s.Open();
Console.Writeline("Press ENTER to end service");
Console.Readline();
s.Close();
}
}
Since the class ReservationHost includes a Main method, it will run as a distinct process. To host the example RentalReservations service, this method must create a new instance of the class ServiceHost, passing in the type of RentalReservations. Once an instance of this class is created, the only thing required to make the service available is to call the Open method on that instance. WCF will now automatically direct requests from clients to the appropriate methods in the RentalReservations class.
To allow a WCF service to process requests from its clients, the process that hosts it must remain running. With WAS-hosted services, the standard process ensures the host remains running, but a hosting application must solve this problem on its own. In this simple example, the process is kept running through the straightforward mechanism of waiting for input from a console user. In a more realistic case, a WCF service hosted in this way would be running in a Windows service, allowing it to be started when a system boots, or be hosted in a GUI application, such as those built with Windows Forms or the forthcoming Windows Presentation Foundation.
In the example above, the service is explicitly closed by calling ServiceHost’s Close method. That isn’t required in this simple case, since the service will be automatically closed when the process ends. In a more complex situation, however, such as a process that hosts multiple WCF services, it might make sense to explicitly close individual services when they’re no longer needed.
Defining Endpoints
Along with defining operations in a WCF service class and specifying a host process to run those operations, a WCF service must also expose one or more endpoints. Every endpoint specifies the following three things:
n A contract name indicating which service contract this WCF service class exposes via this endpoint. A class marked with ServiceContract that implements no explicit interfaces, such as RentalReservations in the first example shown earlier, can expose only one service contract. In this case, all its endpoints will expose the same contract. If a class explicitly implements two or more interfaces marked with ServiceContract, however, different endpoints can expose different contracts, each defined by a different interface.
n An address indicating where this endpoint can be found. Addresses are URLs that identify a machine and a particular endpoint on that machine.
n A binding determining how this endpoint can be accessed. The binding determines what protocol combination can be used to access this endpoint along with other things, such as whether the communication is reliable and what security mechanisms can be used.
Bindings are a critical part of how communication is accomplished. Suppose, for instance, that a service’s creator wishes to allow clients to access that service using either SOAP over HTTP or SOAP over TCP. Each of these is a distinct binding, so the service would need to expose two endpoints, one with a SOAP-over-HTTP binding and the other with a SOAP-over-TCP binding.
To make bindings easier to use, WCF includes a set of predefined bindings, each of which specifies a particular group of options. Developers can configure these standard bindings if necessary, and they can also create wholly new custom bindings that provide exactly what a particular situation requires. Still, most applications will use one or more of the standard bindings that WCF provides. Along with a few more, this set includes the following:
n BasicHttpBinding: Conforms to the Web Services Interoperability Organization (WS-I) Basic Profile 1.0, which specifies SOAP over HTTP. This binding can also be configured to use HTTPS as specified by the WS-I Basic Security Profile 1.0. It can also be configured to send either standard text or the optimized form defined by MTOM.
n WsHttpBinding: Uses SOAP over HTTP, like BasicProfileBinding, but also supports reliable message transfer with WS-ReliableMessaging, security with WS-Security, and transactions with WS-AtomicTransaction. This binding allows interoperability with other Web services implementations that also support these specifications.
n NetTcpBinding: Sends binary-encoded SOAP, including support for reliable message transfer, security, and transactions, directly over TCP. This binding can be used only for WCF-to-WCF communication.
n NetNamedPipesBinding: Sends binary-encoded SOAP over named pipes. This binding is only usable for WCF-to-WCF communication between processes on the same Windows-based machine.
n NetMsmqBinding: Sends binary-encoded SOAP over MSMQ, as described later in this paper. This binding can only be used for WCF-to-WCF communication.
Unlike attributes, which are part of a service’s source code, bindings can be different for different deployments of the same service. There are a few situations where this could be problematic, however. As described later, for instance, whether a service can join an existing transaction passed to it by a client is controlled using bindings. This distinction makes sense, since different deployments of the same service might need to set this value differently. But what if a particular service class always requires this behavior? To make sure that it’s available, a developer can mark the class with the BindingRequirements attribute, specifying that the ability to flow transactions must be provided by all bindings this class uses. If the BindingRequirements attribute is present, WCF will check at runtime to make sure that the service’s bindings provide the required behavior.

The figure on the previous page shows example values for each of the three elements[2] in an endpoint for the first RentalReservations service shown earlier. The name of the service’s contract is RentalReservations, which is the name of the class that implements this service, and the binding is BasicHttpBinding. Assuming this service is hosted using either IIS or WAS, installed in the virtual directory reservation as described earlier, and running on a machine named fabricam.com, its address might be http://www.fabricam.com/reservation/reserve.svc.
Specifying Endpoints
Unlike contracts, endpoints aren’t defined using attributes. It can sometimes be useful to specify endpoints in code, however, so WCF provides a way to do this. A service that is explicitly hosted in a ServiceHost object, for instance, can use this object’s AddEndpoint method to create an endpoint. If this were done in the example shown earlier, the Main method might now look like this:
public static void Main()
{
ServiceHost s =
new ServiceHost(typeof(RentalReservations));
s.AddEndpoint(typeof(RentalReservations),
new BasicHttpBinding(),
"http://www.fabricam.com/reservation/reserve.svc");
s.Open();
Console.Writeline("Press ENTER to end service");
Console.Readline();
s.Close();
}
The three parameters to AddEndpoint are the contract, binding and address of the new endpoint.
Even though defining endpoints programmatically is possible, the most common approach will probably be to use a configuration file associated with the service. Endpoint definitions embedded in code are difficult to change when a service is deployed, yet some endpoint characteristics, such as the address, are very likely to differ in different deployments. Defining endpoints in config files makes them easier to change, since it doesn’t require modifying and recompiling the source code for the service class. For services hosted in IIS or WAS, endpoints can be defined in the web.config file, while those hosted independently use the configuration file associated with the application they’re running in (commonly referred to as app.config, although the actual filename varies). If used solely for the first RentalReservations service class shown earlier, this configuration file might look like this:
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<services>
<service type="RentalReservations,RentalApp">
<endpoint
contract="RentalReservations,RentalApp"
binding=”basicHttpBinding”
address=
"http://www.fabricam.com/reservation/reserve.svc"/>
</service>
</services>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
The configuration information for all services implemented by a WCF-based application is contained within the system.serviceModel element. This element contains a services element that can itself contain one or more service elements. This simple example has only a single service, so there is just one occurrence of service. The type attribute of the service element identifies the service class that implements the service this configuration applies to, which in this case is RentalReservations. It also specifies the name of the .NET assembly that implements this service, which here is RentalApp. Each service element can contain one or more endpoint elements, each of which specifies a particular endpoint through which the WCF service can be accessed. In this example, the service exposes only a single endpoint, so only one endpoint element appears. The name of the endpoint’s contract is RentalReservations, which is the name of the class that implements it, and the assembly name is once again included here. If this configuration file were for the second RentalReservations service class shown earlier, which defined its service contract using an explicit interface, the value of the type attribute would remain the same, but the value of contract would instead be IReservations, the name of this explicit interface, rather than RentalReservations. The binding specified here is basicHttpBinding, as shown earlier. And assuming RentalReservations is hosted using IIS or WAS, an address is created automatically, so there’s no need to specify one in this config file. Explicitly including it is legal, however, as this example shows.
Using Endpoints: An Example
To get a more concrete sense of how endpoints can be used, think once more about the rental car reservation application. To meet the diverse communication requirements of its clients, this application, implemented in the RentalReservations service class, will probably choose to expose several endpoints, each with a different binding:
n For communication with the call center client application, high performance and full functionality including strong security and transactions are required. Since both the RentalReservations class and the call center client are built on WCF, a good binding option for the endpoint this client accesses would be NetTcpBinding. It’s the most efficient choice, and it also provides a full set of communication behaviors, including reliable transfer, strong security, and transactions.
n For communication with the existing J2EE-based reservation application, a binding that uses standard SOAP on the wire is required. If the application and the platform it runs on support some or all of the WS-* specifications, the endpoint used by this client might choose WsHttpBinding. This would allow reliable, secure, and transactional communication between the two applications. If this application and the platform it runs on support only standard SOAP matching the WS-I Basic Profile, however, the endpoint it uses to access the rental car reservation application would use BasicHttpBinding. If transport security is required, this binding could be configured to use HTTPS instead of plain HTTP. How this is done is shown later in this paper.
n For communication with the various partner applications, different endpoints might be used, depending on the binding requirements. For example, the most basic Web services client could access an endpoint that used BasicHttpBinding, while one that also supported transport security might use this same binding configured to use HTTPS. A partner application that was capable of using the WS-* technologies could instead use an endpoint with WsHttpBinding. It’s worth pointing out, however, that even a partner application built on WCF and the .NET Framework 2.0 would find the NetTcpBinding problematic to use across the Internet. Communication with this binding uses a port other than port 80, so traffic using it cannot get through most firewalls.
For this simple application, all of these endpoints would specify the same service contract, because all provide the same set of exposed services. Each endpoint would typically have its own unique address, however, since each one must be explicitly identified by the clients that use it.
Creating a WCF Client
Creating a basic WCF service isn’t especially complicated. Creating a WCF client is even simpler. All that’s required is to create a local stand-in for the service, called a proxy, that’s connected to a particular endpoint on the target service, and then invoke the service’s operations via the proxy. The figure below shows how this looks.
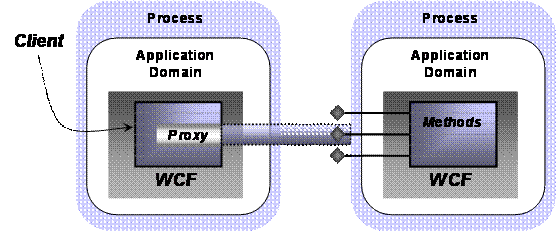
Creating a proxy requires knowing exactly what contract is exposed by the target endpoint, and then using the contract’s definition to generate the proxy. In WCF, this process can be performed by a tool called svcutil. If the service is implemented using WCF, svcutil can access the service’s DLL to learn about the contract and generate a proxy. If only the service’s WSDL definition is available, svcutil can read this to produce a proxy. If only the service itself is available, svcutil can access it directly using either WS-MetadataExchange or a simple HTTP GET to acquire the service’s WSDL interface definition, and then generate the proxy.
However it’s generated, the client can create a new instance of the proxy, and then invoke the service’s methods using it. Following is a simple example of how a client of the RentalReservations class might make a reservation for a compact car at Heathrow Airport in the autumn of 2005:
using System.ServiceModel;
public class RentalReservationsClient
{
public static void Main()
{
int confirmationNum;
RentalReservationsProxy p = new RentalReservationsProxy();
if (p.Check(1, 349, “9/30/05-10/10/05”)) {
confirmationNum = p.Reserve(1, 349, “9/30/05-10/10/05”);
}
p.Close();
}
}
In this simple example, the code for compact cars is 1, the location Heathrow Airport is designated as 349, and dates are given in the American style. All that is required is to verify availability by calling the Check method on the proxy, and then make the reservation by calling Reserve. The final call to the proxy’s Close method is not strictly required in this simple case, but it is good programming practice to explicitly clean up the communications infrastructure that has been created. In fact, a proxy actually creates a communication path called a channel with a specific service endpoint, and closing the proxy tears down this channel. For clients that require more direct control over their communication, it’s also possible to no use proxies at all and instead work directly with channels.
One more thing remains to be specified by the client: the exact endpoint it wishes to invoke operations on. Like a service, the client must specify the endpoint’s contract, its binding and its address, and this is typically done in a config file. In fact, if enough information is available, svcutil will automatically generate an appropriate client configuration file for the target service.
Other Aspects of WCF
The basics of services and clients are fundamental to every WCF application. Most of those applications will also use other aspects of this technology, however. This section describes some of these additional features.
Messaging Options
The simple examples shown so far all assume a synchronous remote procedure call (RPC) approach to client/service interaction. WCF supports this option, but it’s not the only choice. SOAP is a message-oriented protocol, which means that it can support a variety of programming models. WCF supports several possibilities along with traditional RPC, including the following:
n Asynchronous RPC, with non-blocking paired calls carrying lists of typed parameters.
n Traditional messaging, with non-blocking calls carrying a single message parameter. Each channel provides a Send and Receive method, and WCF defines a standard Message class that can be used to directly work with XML messages.
n Direct manipulation of SOAP messages using the WCF-defined attribute MessageContract. Using two related attributes, MessageHeader and MessageBody, an application can explicitly access the contents of the SOAP message’s header and body.
To allow creating a method that sends information but doesn’t block waiting for a response, the OperationContract attribute has a property called IsOneWay. Methods marked with this attribute and property can have only input parameters and must return void. Here’s an example:
[OperationContract(IsOneWay=true)]
void CarAvailableNow(int vehicleClass, int location);
With this method, the caller gets nothing in return—it’s one-way communication. One-way methods like this are useful, for instance, as a way to send unsolicited events. Suppose, for instance, that the call center client application wished to be informed whenever a car had become available in a previously sold-out location. That client might implement a WCF service contract containing the CarAvailableNow method, and then let the rental car reservation application invoke it as new cars became available.
It’s also possible to link together calls to methods, whether one-way or normal two-way methods, allowing both sides of the communication to act as client and service. To do this, each side implements a contract that’s linked with its partner, resulting in what are called duplex contracts. WCF provides special bindings for handling this case, such as WsDualHttpBinding for duplex contracts that use standard interoperable SOAP.
Controlling Local Behavior
Many aspects of WCF, such as contracts, bindings and more, are related to communication between a service and its clients. Yet there are also parts of a service’s behavior that are essentially local. How is concurrent access to a service instance managed, for example, and how is that instance’s lifetime controlled? To allow developers to set local behaviors like these, WCF defines two primary attributes, both of which have a number of properties. One of these attributes, ServiceBehavior, can be applied to classes that are also marked with the ServiceContract attribute. The other, OperationBehavior, can be applied to methods in a service class that are also marked with the OperationContract attribute.
The ServiceBehavior attribute has various properties that affect the behavior of the service as a whole. For example, a property called ConcurrencyMode can be used to control concurrent access to the service. If set to Single, WCF will deliver only one client request at a time to this service, i.e., the service will be single-threaded. If this property is set to Multiple, WCF will deliver more than one client request at a time to the service, each running on a different thread. Similarly, ServiceBehavior’s InstanceMode property can be used to control how instances of a service are created and destroyed. If InstanceMode is set to PerCall, a new instance of the service will be created to handle each client request, and then destroyed when the request is completed. If it’s set to PrivateSession, however, the same instance of the service will be used to handle all requests from a particular client. (Doing this also requires setting ServiceContract‘s Session attribute to true and choosing a binding that supports sessions.)
Suppose, for example, that the developer decided that the RentalReservations class should be multi-threaded and use the same instance for each call from a particular client. The class’s definition would then look like this:
using System.ServiceModel;
[ServiceContract(Session=true)]
[ServiceBehavior(
ConcurrencyMode=Multiple,
InstanceMode=PrivateSession)]
class RentalReservations { ... }
Similarly, properties on the OperationBehavior attribute allow controlling the impersonation behavior of the method that implements this operation, its transactional requirements (described later), and other things.
Security
Exposing services on a network, even an internal network, usually requires some kind of security. How can the service be certain of its client’s identity? How can messages sent to and from a service be kept safe from malicious changes and prying eyes? And how can access to a service be limited to only those authorized to use it? Without some solution to these problems, it’s too dangerous to expose many kinds of services. Yet building secure applications is difficult. Ideally, there should be straightforward ways to address common security scenarios, along with more fine-grained control for applications that need it.
To help achieve this, WCF provides the core security functions of authentication, message integrity, message confidentiality, and authorization. All of these depend fundamentally on the notion of identity: who is this user? Establishing an identity for a client or service requires supplying credentials such as a username and password, an X.509 certificate, or something else. A client or service can do this by directly invoking a WCF function, by using a config file, or in other ways, such as by referencing a certificate store. However it is done, establishing an identity is an essential part of using WCF security.
Establishing identity for a client or service is relatively simple. Without a well-designed technology, however, other aspects of distributed security can get very complicated very fast. A primary goal of WCF’s designers was to make building secure applications easy. To allow this, WCF’s approach to authentication, data integrity and data privacy relies on bindings. Rather than require developers to insert the right attributes to secure each class and method, they can instead just use a binding that provides the right set of security services. A developer’s choices include the following:
n Use a standard binding that directly supports security. For example, applications that require end-to-end security for messages that go through multiple SOAP intermediaries can use a binding that supports WS-Security, such as WsHttpBinding.
n Use a standard binding that optionally supports security, then configure it as needed. For example, applications that need only transport-based security can choose BasicHttpBinding, configuring it to use HTTPS rather than HTTP. It’s also possible to customize other more-advanced security behaviors. For example, the authentication mechanism used by a binding such as WsHttpBinding can be changed if desired.
n Create a custom binding that provides exactly the security behavior a developer needs. Doing this is not for the faint of heart, but it can be the right solution for some advanced scenarios.
n Use a standard binding that provides no support for security, such as BasicHttpBinding. While using no security is a risky thing to do, it can be the only option in some situations.
For example, suppose the RentalReservations service wished to expose an endpoint that used the BasicHttpBinding using HTTPS rather than HTTP. The configuration file that defined this endpoint would look like this:
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<services>
<service
type="RentalReservations,RentalApp"
<endpoint
contract="RentalReservations,RentalApp"
binding="basicHttpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="UsingHttps"
address=
”http://www.fabricam.com/reservation/reserve.svc"/>
</service>
</services>
<bindings>
<basicHttpBinding>
<binding
configurationName="UsingHttps"
securityMode="Https"/>
</basicHttpBinding>
</bindings>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
Unlike the configuration file shown earlier, which used just the standard basicHttpBinding, this version includes the bindingConfiguration attribute in the endpoint element. The configuration this attribute references, here given the name UsingHttps, is defined later in the config file within its bindings element. This configuration sets basicHttpBinding’s securityMode property to Https, causing all communication with this endpoint to use HTTPS rather than standard HTTP.
A WCF service can also control which clients are authorized to use its services. To do this, WCF just relies on existing authorization mechanisms in the .NET Framework. A service can use the standard PrincipalPermission attribute, for example, to define who is allowed to access it.
Helping developers build more secure applications without exposing them to overwhelming complexity has proved to be challenging in the past. By providing both a straightforward approach for the most common cases and fine-grained control for more complex situations, WCF aims at hitting this target in a usable and effective way.
Transactions
Handling transactions is an important aspect of building many kinds of business logic. Yet using transactions in a service-oriented world can be problematic. Distributed transactions assume a high level of trust among the participants, so it often isn’t appropriate for a transaction to span a service boundary. Still, since there are situations where combining transactions and services makes sense, WCF includes support for this important aspect of application design.
Transactions in the .NET Framework 2.0
The transaction support in WCF builds on enhancements provided in version 2.0 of the .NET Framework. The forthcoming release includes System.Transactions, a new namespace focused solely on controlling transactional behaviors. Developers will most often use the services of System.Transactions in concert with an execution context, a construct that’s new in version 2.0 of the .NET Framework. An execution context allows the specification of common information such as a transaction that applies to all code contained within a defined scope. Here’s an example of how an application can use this approach to group a set of operations into a single transaction:
using System.Transactions;
using (TransactionScope ts =
new TransactionScope(TransactionScopeOption.Required)) {
// Do work, e.g., update different DBMSs
ts.Complete();
}
All of the operations within the using block will become part of a single transaction, since they share the transactional execution context it defines. The last line in this example, calling the TransactionScope‘s Complete method, will result in a request to commit the transaction when the block is exited. This approach also provides built-in error handling, aborting the transaction if an exception is raised.
Specifying TransactionScopeOption.Required for the new TransactionScope, as this example does, means that this code will always run as part of a transaction: joining its caller’s transaction if one exists, creating a new one if it does not. Much like Enterprise Services, other options, such as RequiresNew, can also be specified.
Unlike Enterprise Services and its predecessors Microsoft Transaction Services (MTS) and COM+, Systems.Transactions is focused entirely on controlling transactional behavior. There is no required connection between a transaction and the internal state of an object, for example. While Enterprise Services requires an object to be deactivated when it ends a transaction, Systems.Transactions makes no such demand. Since WCF builds on Systems.Transaction, WCF-based applications are also free to manage transactions and object state independently.
Transactions in WCF
WCF-based applications can use the types in System.Transactions directly, or they can control transactions using WCF-defined attributes that rely on System.Transactions under the covers. In the first option, a method marked with the OperationContract attribute might wrap its work in a transaction using TransactionScope, as just described. For example, this method might include a using statement that establishes a transaction scope, and then update two independent databases within that transaction.
Alternatively, a service’s methods can control transactional behavior using an attribute. Rather than explicitly using System.Transactions, a service can use the OperationBehavior attribute described earlier. Suppose, for instance, that the work done by the Reserve method in the RentalReservations class was always transactional. This is certainly plausible, since creating a new reservation might require updating more than one database system. In this case, Reserve could be defined like this:
[OperationContract]
[OperationBehavior(TransactionScopeRequired=true,
TransactionAutoComplete=true)]
private int Reserve(int vehicleClass, int location, string dates)
{
int confirmationNumber;
// logic to reserve rental car goes here
return confirmationNumber;
}
In this example, Reserve is now preceded by the OperationBehavior attribute with the TransactionScopeRequired property set to true. Because of this, all work done within this method will happen inside a transaction, just as if it were inside the transaction scope of the using block shown earlier. And because the TransactionAutoComplete property is also set to true, the transaction will automatically vote to commit if no exception is raised.
If the client invoking this method is not running inside a transaction, the Reserve method will run in its own transaction — there’s no other choice. But suppose the client is already part of an existing transaction when it calls Reserve. Will the work done by the Reserve method join the client’s transaction, or will it still run inside its own independent transaction? The answer depends on whether this service can accept a transaction context passed by the client, an option controlled using bindings. Some bindings, such as WsHttpBinding and NetTcpBinding, can be configured to include a transactionFlow element that determines whether a service can accept a transaction context passed by the client. If the binding used by the example service does this and the client passes in a transaction context, the work done by Reserve will become part of the client’s transaction. If not, this method’s work will remain in its own transaction.
To see how this might be used, think once again about the rental car reservation application. The endpoint that the call center client application accesses would likely be configured to accept a transaction context flowed from the client, since this application is trusted enough to engage the reservation system’s methods in a transaction. In fact, since this client is probably created by the same team producing the reservation application itself, it’s safe to assume that it won’t keep a transaction open — and thus lock the data that transaction uses — for too long. Similarly, the J2EE-based existing reservation application would access the rental car reservation system using an endpoint whose binding is configured to accept a transaction context flowed from the client. This application is also trusted to include the reservation system’s methods in transactions, since it’s controlled by the same company. But all the endpoints accessed by partner applications are likely to have bindings that will not accept a transaction context flowed from the client. Since these partner applications are owned by other organizations, they are unlikely to be trusted enough to engage the reservation application’s methods in transactions.
Finally, it’s worth emphasizing that applications built on WCF can participate in transactions that include applications running on non-WCF platforms. For example, a WCF-based application might start a transaction, update a record in a local SQL Server database, then invoke a Web service implemented on a J2EE-based application server that updates a record in another database. If this service is transactional and the platform it’s running on supports the WS-AtomicTransaction specification, both database updates can be part of the same transaction. Like security and reliable messaging, WCF transactions work in the heterogeneous world that Web services make possible.
Queuing
Using a binding such as WsHttpBinding, a WCF-based application can communicate reliably with another application built on WCF or any other Web services platform that implements WS-ReliableMessaging. But while the technology this specification defines guarantees reliable end-to-end delivery of a SOAP message, it does not address message queuing. With queuing, an application sends a message to a queue rather than directly to another application. When the receiving application is ready, it can read the message from the queue and process it. Allowing this kind of interaction is useful, for example, when the sender of a message and its receiver might not be running at the same time.
Accordingly, WCF provides support for message queuing. This support is built on top of MSMQ[3], which means that unlike most other aspects of WCF, such as reliable messaging, security and transactions, WCF queuing does not interoperate directly across vendor boundaries (although an MSMQ-MQSeries bridge is available).
To use WCF queuing, a developer can create a standard WCF service class, marked as usual with ServiceContract. The operations in this class’s service contract have some limitations, however. In particular, they must all be marked as one-way, which means that no response is returned. This isn’t surprising, since invoking a queued operation sends a message into a queue rather than to its ultimate receiver, so waiting for an immediate response wouldn’t make much sense. And like any other service class, queued WCF-based applications expose endpoints. These endpoints use bindings such as NetMsmqBinding, which allows communication with other queued WCF-based applications, or MsmqIntegrationBinding, which allows a queued WCF-based application to interoperate with a standard MSMQ application that doesn’t use WCF. WCF queuing also supports other traditional aspects of queued environments, such as dead letter queues and handling of poison messages.
Queuing is the right approach for a significant set of distributed applications. WCF’s support for this communication style allows developers to build queued applications without needing to learn an entirely separate queuing technology.
Extensibility
Most users will be perfectly happy with WCF’s standard functionality. Advanced developers, however, will in some cases need to extend what WCF provides. To allow this, WCF offers several extensibility options.
For example, it’s possible to create a custom channel. As described earlier, WCF clients and servers rely on channels to communicate (although clients will often hide the channel beneath a proxy). If necessary, a developer can create a channel that meets the specific requirements of her application. For example, suppose that a particular scenario requires an application to send SOAP messages over a protocol that isn’t supported by WCF, such as SMTP or a proprietary message queuing product. By creating a custom channel, the standard WCF programming model could be used on top of this existing communication technology. It’s also possible to directly insert information into the SOAP headers sent by WCF applications, such as custom elements for non-standard SOAP-based protocols.
Another extensibility option is to create a validator. Each validator defines an attribute and some associated code. That code is run every time an instance of a service that contains the attribute is started, giving the code the opportunity to check some aspect of the service. A validator might verify that a particular service has no endpoints that use bindings without security, for instance, or ensure that no duplex contracts are supported, or verify some other rule that’s meaningful in a particular organization or application. If a validator indicates that the conditions it’s checking are not met, the service will not execute. WCF itself actually uses this approach: the BindingRequirements attribute described earlier is implemented as a validator.
WCF also contains a number of behaviors that can be customized or adjusted in various ways using either custom attributes or config files. It’s possible to create an attribute that causes custom code to be executed whenever a message is sent or received, for instance, allowing WCF to be used in the style of aspect-oriented programming. It’s also possible to customize behaviors in other ways, including things such as substituting a custom serializer in place of the serializers that WCF provides. For applications that require specialized behaviors, these options can be essential.
Tool Support: WCF and Visual Studio
Like the rest of the .NET Framework, WCF has a tight relationship with Visual Studio. WCF will ship after Visual Studio 2005 is released, but before the next version of Visual Studio, code-named Orcas, becomes available. Accordingly, an extension pack for Visual Studio 2005 is scheduled to be released that adds WCF-specific support to this standard development tool. In WCF’s first beta release, the extension pack includes things such:
n IntelliSense technology for WCF types, allowing automatic statement completion in C#, Visual Basic, and other .NET languages, just as with other .NET Framework technologies
n IntelliSense for WCF configuration, allowing statement completion when creating XML elements in config files
n Context-sensitive Help triggered by putting the cursor over any WCF type and hitting F1
n Templates for creating a WCF service, a .svc file and more
n An extension to the current Add Web Reference function that enables automatic generation of a WCF proxy to an existing Web service
More tool support is planned for the final release of WCF.
WCF represents a modern approach to creating distributed applications in the era of reliable, security-enhanced, and transactional services. A key point to understand, however, is that installing WCF will not break any existing applications. Current code running on ASMX, .NET Remoting, and the other technologies whose functionality is subsumed by WCF will continue to run, so there is no requirement to upgrade to WCF. But for organizations with investments in current Microsoft technologies, an obvious question remains: What happens to existing code written using the technologies that preceded WCF?
For each of the current technologies whose future is deeply affected by the advent of WCF, developers need to understand two things: whether applications built on this technology will interoperate with applications built on WCF, and how much work it will be to port applications from this technology to the WCF environment. Here’s a short description of how each technology addresses these issues:
n ASP.NET Web Services (ASMX): Web services built with ASMX will interoperate with WCF applications. Since ASP.NET Web services and WCF both support standard SOAP, this shouldn’t be surprising. Moving existing ASP.NET Web services code to WCF will require some mechanical work, but should still be straightforward. The basic structure of the two technologies is quite similar, so for the most part only attributes and configuration files will need to be changed. Some advanced features, however, such as SOAP Extensions, will not be directly portable to WCF. Instead, they’ll need to be rewritten using the extensibility options that WCF provides.
n .NET Remoting: Applications built on .NET Remoting will not interoperate with applications built on WCF— their wire protocols aren’t compatible. Moving existing .NET Remoting code to WCF will require some effort, but it will be possible. Anyone who has built custom .NET Remoting extensions, however, such as channels and sinks, will find that this code won’t port to the new world. Similar extensions are possible in WCF, but the interfaces for doing it don’t match those in .NET Remoting.
n Enterprise Services: To allow an existing Enterprise Services application to interoperate with WCF clients (or other Web-services-based software), developers can identify exactly which interfaces in that application should be exposed. Using a WCF-supplied tool, service contracts can then be automatically created for those interfaces and exposed via WCF. For existing clients of Enterprise Services applications that are not built on the .NET Framework (and for other purely COM-based clients), a WCF moniker is provided to allow straightforward access to Web services. The effort required to port existing Enterprise Services applications to run directly on WCF will be similar to what’s required to port ASMX applications. Much of the work, though not all of it, will be straightforward mechanical changes to attributes and namespaces.
n Web Services Enhancements: WSE is Microsoft’s tactical solution for implementing Web services applications that require some or all of the functions provided by the WS-* specs. Applications built using WSE 1.0 and WSE 2.0 will not interoperate with applications built on WCF. However, applications built on WSE 3.0 will interoperate with WCF applications. For portability, the story is similar to the technologies already described: some amount of effort will be required to move existing code from WSE to WCF, although this effort will be minimized for applications that use the final WSE version.
n Microsoft Message Queuing: Because WCF’s queuing functions are built on MSMQ, queued applications built on WCF can interoperate with queued applications built directly on MSMQ. Porting applications from the System.Messaging namespace provided with the original .NET Framework will require some work, since this earlier interface is different from what WCF provides. Once WCF ships, developers should use it rather than System.Messaging to create most MSMQ-based applications.
To provide a concrete example of what moving to WCF entails, the following section shows how the RentalReservations class, including a transactional Reserve method, might have been defined using ASMX:
using System.Web.Services;
class RentalReservations
{
[WebMethod]
public bool Check(int vehicleClass, int location, string dates)
{
bool availability;
// logic to check availability goes here
return availability;
}
[WebMethod(TransactionOption=TransactionOption.Required)]
private int Reserve(int vehicleClass, int location,
string dates)
{
int confirmationNumber;
// logic to reserve rental car goes here
return confirmationNumber;
}
[WebMethod]
private bool Cancel(int confirmationNumber)
{
bool success;
// logic to cancel reservation goes here
return success;
}
public int GetStats()
{
int numberOfReservations;
// logic to determine the current number of reservations goes here
return numberOfReservations;
}
}
Compare this with a WCF-based implementation of the same class:
using System.ServiceModel;
[ServiceContract(FormatMode=ContractFormatMode.XmlSerializer)]
class RentalReservations
{
[OperationContract]
public bool Check(int vehicleClass, int location, string dates)
{
bool availability;
// logic to check availability goes here
return availability;
}
[OperationContract]
[OperationBehavior(AutoEnlistTransaction=true,
AutoCompleteTransaction=true)]
private int Reserve(int vehicleClass, int location, string dates)
{
int confirmationNumber;
// logic to reserve rental car goes here
return confirmationNumber;
}
[OperationContract]
private bool Cancel(int confirmationNumber)
{
bool success;
// logic to cancel reservation goes here
return success;
}
public int GetStats()
{
int numberOfReservations;
// logic to get the current number of reservations goes here
return numberOfReservations;
}
}
The differences are simple:
n The using statement references a different namespace;
n The class is marked with ServiceContract (and due to a difference in serialization defaults, this attribute’s FormatMode property must be set as shown);
n The exposed operations use the OperationContract attribute rather than WebMethod;
n The Reserve method is made transactional using OperationBehavior rather than a property on WebMethod.
These changes are straightforward. In fact, writing a script that programmatically changed existing ASMX applications wouldn’t be too difficult.
As this example suggests, before WCF is available, the best technology choice for distributed .NET applications that do not need queuing is probably ASMX. It’s simple to use, and it provides the smoothest upgrade path to WCF. Enterprise Services might also make sense for applications that need the things it provides, such as distributed transactions, while MSMQ remains the right choice for queued applications. .NET Remoting, however, should be used primarily for communication between two application domains in the same process. In most other cases, ASMX is a better choice for direct application-to-application communication.
Introducing new software always has an impact on what already exists. By providing a common foundation for building service-oriented applications, WCF offers a simpler, more consistent platform for developers. The goal of WCF’s creators is to make the transition as smooth and as simple as possible.
Because it unifies today’s different approaches to communication, WCF simplifies the creation of distributed applications on Windows. Because it implements SOAP and the most important WS-* specifications, WCF provides full-featured interoperability with other Web services platforms. And because it offers explicit support for a service-oriented approach, WCF gives developers a natural environment for building modern software.
Service-oriented applications are becoming the norm, and WCF will soon be a mainstream technology for Windows. For anyone who creates applications in this world, WCF qualifies as a significant step forward.
David Chappell is Principal of Chappell & Associates (www.davidchappell.com) in San Francisco, California. Through his speaking, writing, and consulting, he helps technology professionals around the world understand, use, market, and make better decisions about enterprise software.